Autonomous sensor systems
Contact: Karen Dowling

Sensor systems are used for measuring, monitoring and control. Autonomous sensor systems are sensor systems in which distributed sensor nodes contain local signal and data pre-processing capabilities. Thus, self-testing, auto-calibration, filtering, data compression, etc., within sensor nodes without or with very limited external intervention is crucial. In many applications, wiring is not possible, unreliable or undesirable, which makes the powering of sensors a major issue and calls for ultra-low power electronics and smart design at all levels in the system.
In IoT applications, sensors operate in a network. Limited power resources favor power-efficient communications. Sensors can communicate only with neighboring nodes, creating a dynamic and complex network that relies on self-organizing and self-healing capabilities.
In biomedical applications, the sensors need to be miniaturized and packaged to be bio-compatible or implantable, as e.g. with smart (multi-modal) catheters or electroceuticals, which combine sensing, local data processing, and actuation.
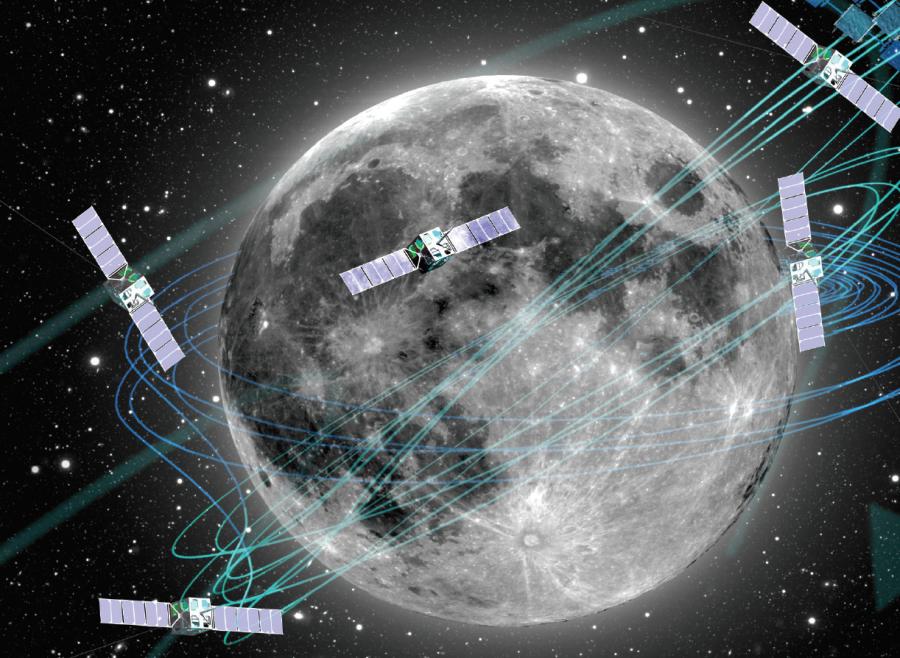
In other applications (autonomous driving or flying enabled by a variety of radar sensors distributed over many nodes), the focus is on robustness and reliability in view of a very dynamic network, and optimal fusion of different sources of information. With TUE we collaborate on a program to realize a low-frequency radio telescope in space using a swarm of nano-satellites (OLFAR). Emerging technologies such as neuromorphic computing and structured data science are expected to play an important role in future.
Projects under this theme
Sustainable Power Solution for Smart Bearings in Wind Turbine Generators
In this project, we develop energy harvesting devices and integrated circuits and systems for sensor rollers used in giant wind turbine generators.
AQUAFIND
Distributed localisation and formation control of drones
ShapeFuture
Robust inference and decision making for automated vehicles.
Model-driven decision lab
Data and model-driven decision making for the Dutch police
Towards robust perception of radar images
Machine learning and Signal Processing for radar systems (digital radar, millimeter-wave radar), automotive sensors, and related applications
Reliable POwerDown for Industrial Drives
The pioneering EU research project R-PODID started on the 1st of September 2023. This KDT JU co-funded project aims to develop an automated, cloudless, short-term fault-prediction for electric drives, power modules, and power devices, that can be integrated into power converters.
Moonshot
Science, technology and Social solutions for Lunar missions
Signal processing for environment-aware radar
In future, cars will exploit multiple radars towards autonomous driving. Before this becomes a reality, several challenges will have to be solved.
AGRARSENSE
Sustainable and Miniature Power Solutions for Future Internet-of-Things
Odour Based Selective Recognition of Veterinary Diseases
Delft Sensor AI Lab
Bringing AI to sensor networks
Cooperative Relative Navigation of Multi-agent Systems
Develop algorithms for multi-target position, time and orientation tracking in a mobile network of multi-agent systems
Next-generation chip assembly processes
Developing technology for ultra-high throughput and sustainable chip assembly processes.
Compact modelling of high-tech systems for health management and optimization along the supply chain
In-vehicle health monitoring
Coded-Radar for Interference Suppression in Super-Dense Environments
CRUISE will address the challenges regarding spectrum crowding and ensures proper radar signal detection, accurate ranging, Doppler and azimuth measurements, and object classification in a highly-occupied frequency spectrum
History
Automotive Intelligence for Connected Shared Mobility
Architectures for embedded intelligence and functional virtualization for connected and shared mobility using trustworthy AI
Distributed Artificial Intelligent Systems
Running existing algorithms on vastly distributed edge devices
Challenging environments tolerant smart systems for IoT
Intelligent Reliability 4.0
Airborne data collection on resilient system architectures
Develop algorithms to realize efficient, robust, cost-effective perception and control for autonomous navigation of drones
Graphene Flagship core 3: Transferless graphene in sensing applications
Internet of Things (IoT) security through machine learning and data sharing
NewControl
Virtual platforms for perception and control in highly automated vehicles, based on safety by design
High Performance Vehicle Computer and Communication System for Autonomous Driving
Solid State Lighting reliability for automotive application
PIPP OLFAR: Breakthrough technologies for Interferometry in Space
Combine multiple satellites into one single scientific instrument: a radio telescope in space
Programmable Systems for Intelligence in Automobiles
(a) fail-operational sensor-fusion framework, (b) dependable embedded E/E architectures, (c) safety compliant integration of AI approaches for object recognition, scene understanding, and decision making
Monolithically integrated SiC sun sensor for Space
Task-cognizant sparse sensing for inference
Low-cost sparse sensing designed for specific tasks
Low-frequency distributed radio telescope in space
Below 15 MHz, the ionosphere blocks EM signals from the sky. Therefore, can we design a radio telescope in space, using a swarm of inexpensive nano-satellites? Accurate localization and clock recovery is important.
News

"Interferometry in space" project granted
NWO-PIPP grant for Raj Rajan
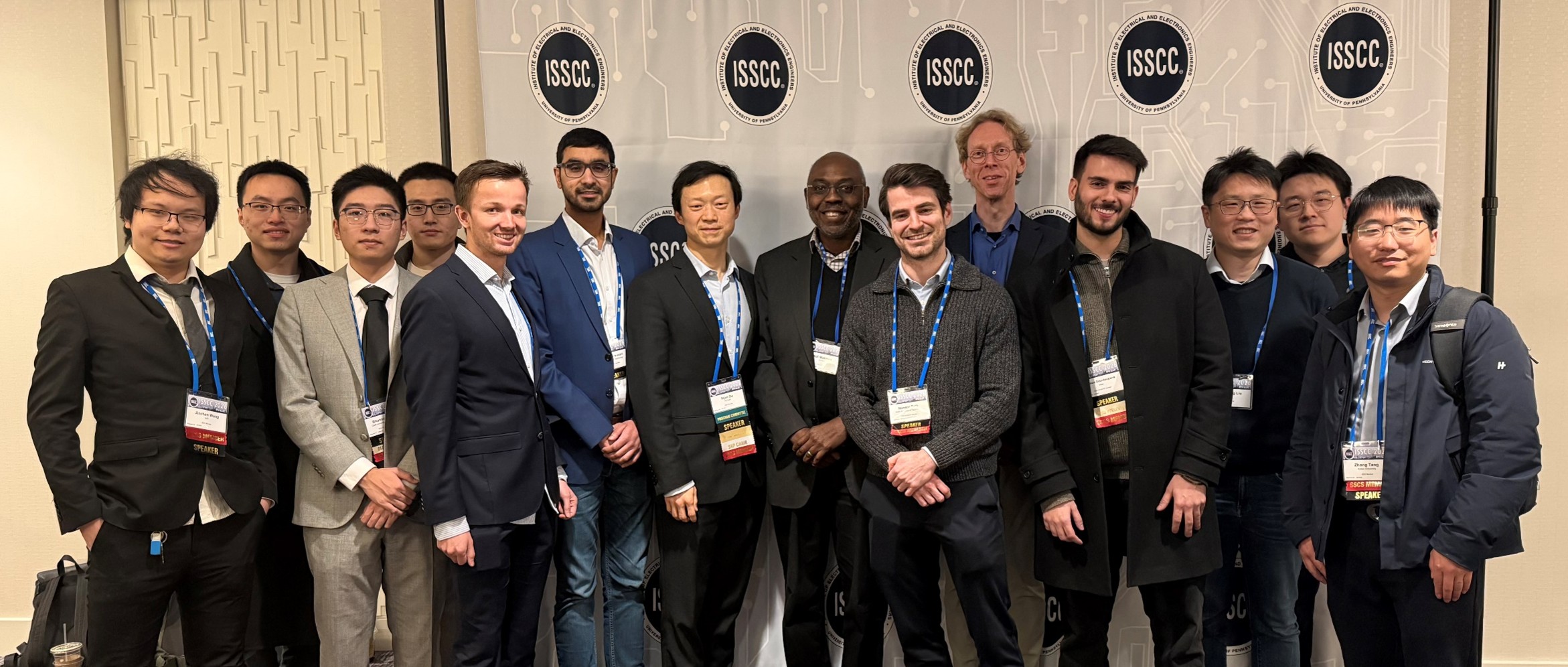

Record presence for the department at ISSCC 2026
At this year’s International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) - the world’s leading conference on chip design (the Chip Olympics), TU Delft presented a record 14 papers and 1 forum talk, out of a total of 39 accepted EU papers.