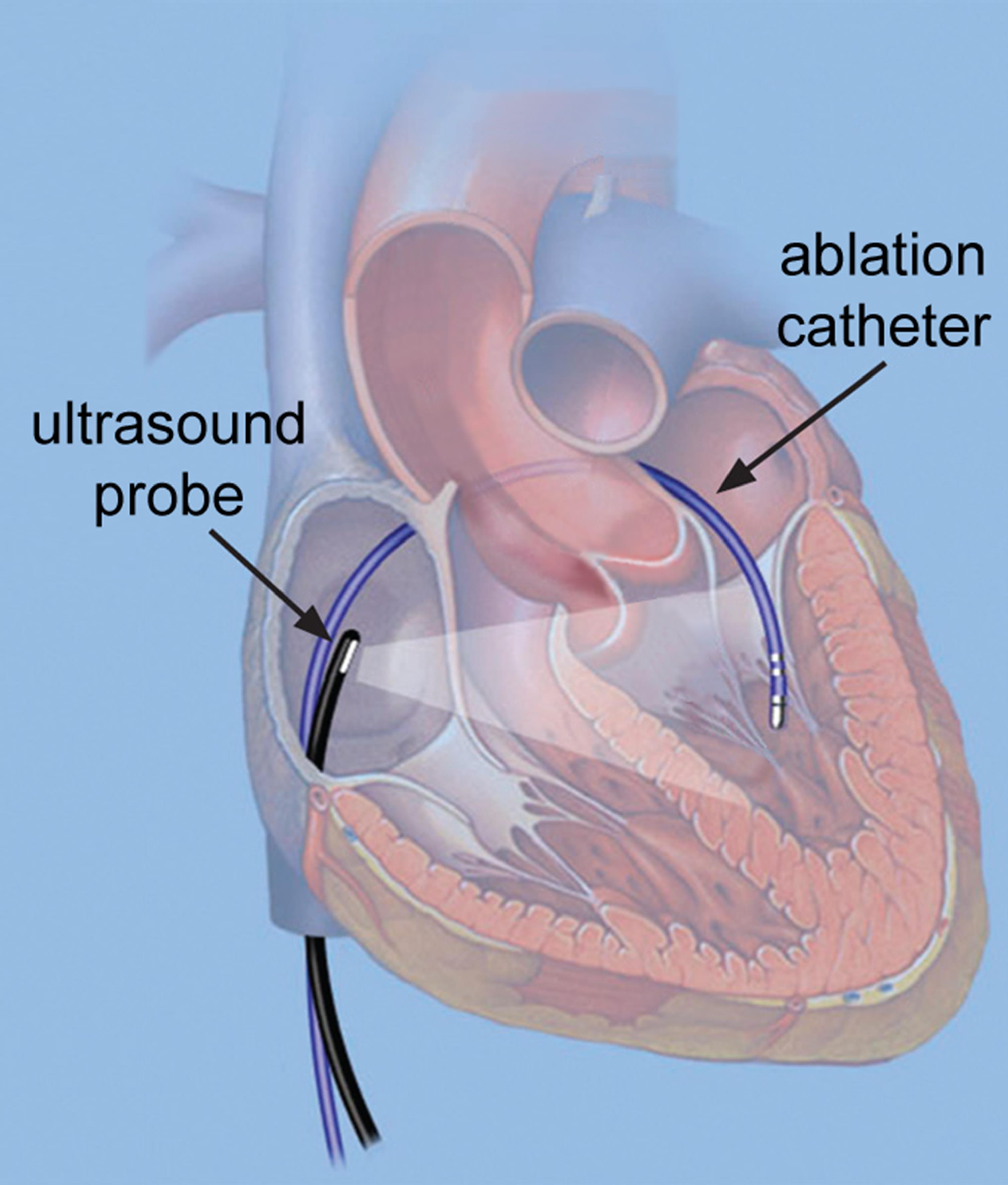
3D Intra-Cardiac Echography
Publications
- An Ultrasound Matrix Transducer for High-Frame-Rate 3-D Intra-cardiac Echocardiography
dos Santos, Djalma Simões; Ossenkoppele, Boudewine; Hopf, Yannick M.; Soozande, Mehdi; Noothout, Emile; Vos, Hendrik J.; Bosch, Johan G.; Pertijs, Michiel A. P.; Verweij, Martin D.; de Jong, Nico;
Ultrasound in Medicine \& Biology,
Volume 50, Issue 2, pp. 285--294, February 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2023.11.001
Abstract: ...
Objective - Described here is the development of an ultrasound matrix transducer prototype for high-frame-rate 3-D intra-cardiac echocardiography. Methods - The matrix array consists of 16 × 18 lead zirconate titanate elements with a pitch of 160 µm × 160 µm built on top of an application-specific integrated circuit that generates transmission signals and digitizes the received signals. To reduce the number of cables in the catheter to a feasible number, we implement subarray beamforming and digitization in receive and use a combination of time-division multiplexing and pulse amplitude modulation data transmission, achieving an 18-fold reduction. The proposed imaging scheme employs seven fan-shaped diverging transmit beams operating at a pulse repetition frequency of 7.7 kHz to obtain a high frame rate. The performance of the prototype is characterized, and its functionality is fully verified. Results - The transducer exhibits a transmit efficiency of 28 Pa/V at 5 cm per element and a bandwidth of 60% in transmission. In receive, a dynamic range of 80 dB is measured with a minimum detectable pressure of 10 Pa per element. The element yield of the prototype is 98%, indicating the efficacy of the manufacturing process. The transducer is capable of imaging at a frame rate of up to 1000 volumes/s and is intended to cover a volume of 70° × 70° × 10 cm. Conclusion - These advanced imaging capabilities have the potential to support complex interventional procedures and enable full-volumetric flow, tissue, and electromechanical wave tracking in the heart. - Pitch-Matched Integrated Circuits for Ultrasound Transducer Arrays
Pertijs, Michiel; Hopf, Yannick; Guo, Peng;
In Imaging Sensors, Power Management, PLLs and Frequency Synthesizers ‐ Advances in Analog Circuit Design,
Springer Science \& Business Media, December 2024. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-71559-4_1
Abstract: ...
While medical imaging using ultrasound is an established field, technical advances are enabling a range of new-use cases and associated new ultrasound imaging devices. Examples include catheters capable of providing real-time 3D images to guide minimally invasive interventions and wearable devices for new monitoring and diagnostic applications. In contrast with conventional probes, which contain little or no electronics, these new devices need to become “smart”: integrated circuits need to be integrated into the probe to interface in a pitch-matched fashion with the many transducer elements (typically 1000+) needed for real-time 3D imaging. This chapter discusses the challenges associated with the design of such pitch-matched integrated circuits, focusing on strategies for channel-count reduction, beamforming, and digitization. The chapter includes a case study of a state-of-the-art catheter-based design for high-frame-rate 3D intracardiac imaging. - An ultrasound matrix transducer for high-frame-rate 3D intracardiac echocardiography
Djalma Simoes dos Santos; Boudewine Ossenkoppele; Yannick M. Hopf; Mehdi Soozande; Emile Noothout; Hendrik J. Vos; Johan G. Bosch; Michiel A. P. Pertijs; Martin D. Verweij; Nico de Jong;
Ultrasound in Medicine \& Biology,
2023. accepted.
Abstract: ...
Objective: This paper presents the development of an ultrasound matrix transducer prototype for high frame rate three-dimensional (3D) intracardiac echocardiography (ICE). Methods: The matrix array consists of 16 ×18 lead zirconate titanate (PZT) elements with a pitch of 160 µm × 160 µm built on top of an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that generates transmission signals and digitizes the received signals. To reduce the number of cables in the catheter to a feasible number, we implement subarray beamforming and digitization in receive and use a combination of time-division multiplexing and pulse amplitude modulation data transmission, achieving an 18-fold reduction. The proposed imaging scheme employs seven fan-shaped diverging transmit beams operating at a pulse repetition frequency of 7.7 kHz to obtain a high frame rate. The performance of the prototype is characterized and its functionality is fully verified. Results: The transducer exhibits a transmit efficiency of 28 Pa/V at 5 cm per element and a bandwidth of 60% in transmission. In receive, a dynamic range of 80 dB is measured with a minimum detectable pressure of 10 Pa per element. The element yield of the prototype is 98%, indicating the efficacy of the manufacturing process. The transducer is capable of imaging at a frame rate of up to 1000 volumes/s and is intended to cover a volume of 70° × 70° × 10 cm. Conclusion: These advanced imaging capabilities have the potential to support complex interventional procedures and enable full-volumetric flow, tissue, and electro-mechanical wave tracking in the heart. - A Pitch-Matched High-Frame-Rate Ultrasound Imaging ASIC for Catheter-Based 3D Probes
Yannick M. Hopf; Djalma Simoes dos Santos; Boudewine W. Ossenkoppele; Mehdi Soozande; Emile Noothout; Zu-Yao Chang; Chao Chen; Hendrik J. Vos; Johan G. Bosch; Martin D. Verweij; Nico de Jong; Michiel A. P. Pertijs;
IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,
Volume 59, Issue 2, pp. 476--491, February 2023. DOI: 10.1109/JSSC.2023.3299749
Abstract: ...
This article presents an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) for catheter-based 3-D ultrasound imaging probes. The pitch-matched design implements a comprehensive architecture with high-voltage (HV) transmitters, analog front ends, hybrid beamforming analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), and data transmission to the imaging system. To reduce the number of cables in the catheter while maintaining a small footprint per element, transmission (TX) beamforming is realized on the chip with a combination of a shift register (SR) and a row/column (R/C) approach. To explore an additional cable-count reduction in the receiver part of the design, a channel with a combination of time-division multiplexing (TDM), subarray beamforming, and multi-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) data transmission is also included. This achieves an 18-fold cable-count reduction and minimizes the power consumption in the catheter by a load modulation (LM) cable driver. It is further explored how common-mode interference can limit beamforming gain and a strategy to reduce its impact with local regulators is discussed. The chip was fabricated in TSMC 0.18-μm HV BCD technology and a 2-D PZT transducer matrix of 16 × 18 elements with a pitch of 160 μm and a center frequency of 6 MHz was manufactured on the chip. The system can generate all required TX patterns at up to 30 V, provides quick settling after the TX phase, and has an reception (RX) power consumption of only 1.12 mW/element. The functionality and operation of up to 1000 volumes/s have been demonstrated in electrical and acoustic imaging experiments. - A prototype matrix transducer for high frame rate 3D intracardiac echography
D. Santos; Y. Hopf; B. Ossenkoppele; J. Bosch; R. Vos; M. Pertijs; N. de Jong; M. Verweij;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
2023. abstract. - Pitch-Matched Integrated Circuits for Ultrasound Transducer Arrays
Y. Hopf; P. Guo; M. Pertijs;
In Proc. Workshop on Advances in Analog Circuit Design (AACD),
April 2023. invited presentation. - A Compact Integrated High-Voltage Pulser Insensitive to Supply Transients for 3D Miniature Ultrasound Probes
Yannick M. Hopf; Boudewine Ossenkoppele; Mehdi Soozande; Emile Noothout; Zu-Yao Chang; Hendrik J. Vos; Johan G. Bosch; Martin D. Verweij; Nico de Jong; Michiel A. P. Pertijs;
IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters,
Volume 5, pp. 166--169, 2022. DOI: 10.1109/lssc.2022.3180071
Abstract: ...
In this paper, a compact high-voltage (HV) transmit circuit for dense 2D transducer arrays used in 3D ultrasonic imaging systems is presented. Stringent area requirements are addressed by a unipolar pulser with embedded transmit/receive switch. Combined with a capacitive HV level shifter, it forms the ultrasonic HV transmit circuit with the lowest reported HV transistor count and area without any static power consumption. The balanced latched-based level shifter implementation makes the design insensitive to transients on the HV supply caused by pulsing, facilitating application in probes with limited local supply decoupling, such as imaging catheters. Favorable scaling through resource sharing benefits massively arrayed architectures while preserving full individual functionality. A prototype of 8 x 9 elements was fabricated in TSMC 0.18 μm HV BCD technology and a 160 μm x 160 μm PZT transducer matrix is manufactured on the chip. The system is designed to drive 65 V peak-to-peak pulses on 2 pF transducer capacitance and hardware sharing of 6 elements allows for an area of only 0.008 mm2 per element. Electrical characterization as well as acoustic results obtained with the 6 MHz central frequency transducer are demonstrated. - Imaging Scheme for 3-D High Frame Rate Intracardiac Echography: a Simulation Study
M. Soozande; B. Ossenkoppele; Y. Hopf; M. Pertijs; M. Verweij; N. de Jong; H. Vos; J. Bosch;
IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control,
Volume 69, Issue 10, pp. 2862--2874, October 2022. DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2022.3186487
Abstract: ...
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia, and normally treated by RF ablation. Intracardiac echography (ICE) is widely employed during RF ablation procedures to guide the electrophysiologist in navigating the ablation catheter, although only 2-D probes are currently clinically used. A 3-D ICE catheter would not only improve visualization of the atrium and ablation catheter, it might also provide 3-D mapping of the electromechanical wave propagation pattern, which represents the mechanical response of cardiac tissue to electrical activity. The detection of this electromechanical wave needs 3-D high frame rate imaging, which is generally only realizable in trade-off with channel count and image quality. In this simulation-based study, we propose a high volume rate imaging scheme for a 3-D ICE probe design that employs 1-D micro-beamforming in elevation direction. Such probe can achieve a high frame rate while reducing the channel count sufficiently for realization in a 10-Fr catheter. To suppress the grating-lobe artifacts associated with micro-beamforming in elevation direction, a limited number of fan-shaped beams with a wide azimuthal and narrow elevational opening angle are sequentially steered to insonify slices of the region of interest. An angular weighted averaging of reconstructed sub-volumes further reduces the grating lobe artifacts. We optimize the transmit beam divergence and central frequency based on the required image quality for electromechanical wave imaging (EWI). Numerical simulation results show that a set of 7 fan-shaped transmission beams can provide a frame rate of 1000 Hz and a sufficient spatial resolution to visualize the electromechanical wave propagation on a large 3-D surface. - A Pitch-Matched ASIC with Integrated 65V TX and Shared Hybrid Beamforming ADC for Catheter-Based High-Frame-Rate 3D Ultrasound Probes
Y. Hopf; B. Ossenkoppele; M. Soozande; E. Noothout; Z. Y. Chang; C. Chen; H. J. Vos; J. G. Bosch; M. D. Verweij; N. de Jong; M. A. P. Pertijs;
In Dig. Techn. Papers IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC),
February 2022. DOI: 10.1109/ISSCC42614.2022.9731597
Abstract: ...
With applications moving to 3D imaging, catheter-based ultrasound probes need to reach a new level of integration. This paper presents the first chip to combine high-voltage transmitters, analog front-ends, micro-beamforming, digitization and transducers, enabling high-frame-rate 3D imaging. Its pitch-matched architecture, made possible by a shared SAR/slope ADC that is 4x smaller and consumes 1.5x less power than the prior art, makes it a scalable solution for future digital imaging catheters. - Transceiver ASIC Design for High-Frame-Rate 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography
Yannick M. Hopf; Boudewine Ossenkoppele; Mehdi Soozande; Emile Noothout; Zu-Yao Chang; Chao Chen; Hendrik J. Vos; Johan G. Bosch; Martin D. Verweij; Nico de Jong; Michiel A. P. Pertijs;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
2022. - A Pitch-Matched ASIC with Integrated 65V TX and Shared Hybrid Beamforming ADC for Catheter-Based High-Frame-Rate 3D Ultrasound Probes
Yannick Hopf; Michiel Pertijs;
In Annual Workshop on Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing (ProRISC),
July 2022. Best presentation award. - Integrated Transceivers for Emerging Medical Ultrasound Imaging Devices: A Review
C. Chen; M. Pertijs;
IEEE Open Journal of the Solid-State Circuits Society,
Volume 1, pp. 104-114, September 2021. DOI: 10.1109/OJSSCS.2021.3115398 - A Compact Integrated High -Voltage Pulserfor 3D Miniature Ultrasound Probes
Yannick Hopf; Mehdi Soozande; Boudewine Ossenkoppele; Hendrik J. Vos; Martin D. Verweij; Johan G. Bosch; Nico de Jong; Michiel A. P. Pertijs;
In Annual Workshop on Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing (ProRISC),
July 2021. poster. - Impact of Bit Errors in Digitized RF Data on Ultrasound Image Quality
Z. Chen; M. Soozande; H. Vos; J. Bosch; M. Verweij; N. de Jong; M. Pertijs;
IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control,
Volume 67, Issue 1, pp. 13-24, January 2020. DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2019.2937462
Abstract: ...
This paper quantitatively analyzes the impact of bit errors in digitized RF data on ultrasound image quality. The quality of B-mode images in both linear and phased array imaging is evaluated by means of three objective image quality metrics: peak signal-to-noise ratio, structural similarity index and contrast-to-noise ratio, when bit errors are introduced to the RF data with different bit-error rates (BERs). The effectiveness of coding schemes for forward error detection and correction to improve the image quality is also studied. The results show that ultrasound imaging is inherently resilient to high BER. The image quality suffers unnoticeable degradation for BER lower than 1E-6. Simple 1-bit parity coding with 9% added redundancy helps to retain similar image quality for BER up to 1E-4, and Hamming coding with 33.3% added redundancy allows the BER to increase to 1E-3. These results can serve as a guideline in the datalink design for ultrasound probes with in-probe receive digitization. With much more relaxed BER requirements than in typical datalinks, the design can be optimized by allowing fewer cables with higher data rate per cable or lower power consumption with the same cable count. - A 64-Channel Transmit Beamformer with ±30V Bipolar High-Voltage Pulsers for Catheter-Based Ultrasound Probes
M. Tan; E. Kang; J.-S. An; Z. Y. Chang; P. Vince; T. Matéo; N. Sénégond; M. A. P. Pertijs;
IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,
Volume 55, Issue 7, pp. 1796-1806, July 2020. DOI: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.2987719
Abstract: ...
This article presents a fully integrated 64-channel programmable ultrasound transmit beamformer for catheter-based ultrasound probes, designed to interface with a capacitive micro-machined ultrasound transducer (CMUT) array. The chip is equipped with programmable high-voltage (HV) pulsers that can generate ±30-V return-to-zero (RZ) and non-RZ pulses. The pulsers employ a compact back-to-back isolating HV switch topology that employs HV floating-gate drivers with only one HV MOS transistor each. Further die-size reduction is achieved by using the RZ switches also as the transmit/receive (T/R) needed to pass received echo signals to low-voltage receive circuitry. On-chip digital logic clocked at 200 MHz allows the pulse timing to be programmed with a resolution of 5 ns, while supporting pulses of 1 cycle up to 63 cycles. The chip has been implemented in 0.18-μm HV Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) technology and occupies an area of 1.8 mm x 16.5 mm, suitable for integration into an 8-F catheter. Each pulser with embedded T/R switch and digital logic occupies only 0.167 mm². The pulser successfully drives an 18-pF transducer capacitance at pulse frequencies up to 9 MHz. The T/R switch has a measured ON-resistance of ~180 Ω . The acoustic results obtained in combination with a 7.5-MHz 64-element CMUT array demonstrate the ability to generate steered and focused acoustic beams. - A Variable-Gain Low-Noise Transimpedance Amplifier for Miniature Ultrasound Probes
E. Kang; M. Tan; J. S. An; Z. Y. Chang; P. Vince; N. Sénégond; T. Mateo; C. Meynier; M. A. P. Pertijs;
IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,
Volume 55, Issue 12, pp. 3157--3168, December 2020. DOI: 10.1109/jssc.2020.3023618
Abstract: ...
This article presents a low-noise transimpedance amplifier (TIA) designed for miniature ultrasound probes. It provides continuously variable gain to compensate for the time-dependent attenuation of the received echo signal. This time-gain compensation (TGC) compresses the echo-signal dynamic range (DR) while avoiding imaging artifacts associated with discrete gain steps. Embedding the TGC function in the TIA reduces the output DR, saving power compared to prior solutions that apply TGC after the low-noise amplifier. The TIA employs a capacitive ladder feedback network and a current-steering circuit to obtain a linear-in-dB gain range of 37 dB. A variable-gain loop amplifier based on current-reuse stages maintains constant bandwidth in a power-efficient manner. The TIA has been integrated in a 64-channel ultrasound transceiver application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) in a 180-nm BCDMOS process and occupies a die area of 0.12 mm². It achieves a gain error below ±1 dB and a 1.7 pA/√ Hz noise floor and consumes 5.2 mW from a ±0.9 V supply. B-mode images of a tissue-mimicking phantom are presented that show the benefits of the TGC scheme. - A 2 pA/√Hz Transimpedance Amplifier for Miniature Ultrasound Probes with 36dB Continuous Time-Gain Compensation
E. Kang; M. Tan; J. An; P. Vince; N. Sénégond; T. Mateo; Cyril Meynier; M. A. P. Pertijs;
In Dig. Techn. Papers IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC),
pp. 354-355, February 2020. - Integrated Front-End Electronics for Miniature Ultrasound Probes
M. Pertijs;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
September 2020. invited paper. - A 1-D CMUT Transducer with Front-end ASIC in a 9 French Catheter for Intracardiac Echocardiography: Acoustic and Imaging Evaluation
T. Matéo; P. Vince; N. Sénégond; M. Tan; E. Kang; M. Pertijs;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
September 2020. DOI: 10.1109/IUS46767.2020.9251715
Abstract: ...
In this work, we report the acoustical characterization of a 9 French (Fr) CMUT-based 1D catheter tip (2.5×12.8 mm2 - 64 elements - 7.5 MHz) embedding a 64 channels analog transceiver ASIC (180 nm HV BCD technology) dedicated to Intra-cardiac Echocardiography. To this end, a Through-Silicon-Via process has been integrated in the CMUT process flow to ensure suitable vertical integration level needed to accommodate with the catheter's form factor. Good overall functioning of essential ASIC functionalities with the CMUT, i.e. transmit, beamforming, and receive, is first reported, starting from elementary characterization up to imaging. Additionally, a comparison with a custom discrete solution based on Commercial Off-The-Shelf components (COTS) to provide suitable CMUT preamplification in receive is performed. Using the same CMUT chip either with the ASIC, either with the COTS, allowed to quantify the benefit brought by the ASIC compared to a more straightforward but less integrated solution. Main results highlight that CMUT-on-ASIC allows to recover a much wider bandwidth (BW), increasing by 3 MHz the -6dB upper limit, and therefore getting closer the theoretical BW of the CMUT itself. Moreover, lower element crosstalk is measured on CMUT-on-ASIC device, showing that the ASIC decreases the electrical coupling compared to the COTS. Finally, noise equivalent pressure measurements in comparison with simulations in realistic ICE configuration promise much higher receive sensitivity with the ASIC solution, hence, confirming its great interest for the CMUT technology compared to less integrated solution, especially for catheter application. - 3D High Frame Rate Imaging Scheme for Ultrasound Carotid Imaging
M. Soozande; M. Mozzaffarzadeh; F. Fool; T. Kim; E. Kang; M. Pertijs; M. Verweij; H. J. Vos; J. G. Bosch; N. de Jong;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
September 2020. abstract. - An Integrated Programmable High-Voltage Bipolar Pulser with Embedded Transmit/Receive Switch for Miniature Ultrasound Probes
M. Tan; E. Kang; J.-S. An; Z. Y. Chang; P. Vince; N. Sénégond; M. A. P. Pertijs;
IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters,
Volume 2, Issue 9, pp. 79-82, September 2019. DOI: 10.1109/LSSC.2019.2938141
Abstract: ...
This letter presents a compact programmable high-voltage (HV) pulser for ultrasound imaging, designed for driving capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTs) in miniature ultrasound probes. To enable bipolar return-to-zero (RZ) pulsing and embedded transmit/receive switching, a compact back-to-back isolating HV switch is proposed that employs HV floating-gate drivers with only one HV MOS transistor each. The pulser can be digitally programmed to generate bipolar pulses with and without RZ, with a peak-to-peak swing up to 60 V, as well as negative and positive unipolar pulses. It can generate bursts of up to 63 pulses, with a maximum pulse frequency of 9 MHz for an 18-pF transducer capacitance. Realized in TSMC 0.18um HV BCD technology, the pulser occupies only 0.167mm2 . Electrical characterization results of the pulser, as well as acoustic results obtained in the combination with a 7.5-MHz CMUT transducer, are presented. - Feasibility of High Frame Rate 3-D Intracardiac Echography using Fan-Beam Transmissions
M. Soozande; B. Ossenkoppele; Y. Hopf; M. A. P. Pertijs; M. D. Verweij; H. J. Vos; J. G. Bosch; N. de Jong;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
IEEE, pp. 1-4, October 2019. - An Integrated Programmable High-Voltage Bipolar Pulser with Embedded Transmit/Receive Switch for Miniature Ultrasound Probes
M. Tan; E. Kang; J.-S. An; Z. Y. Chang; P. Vince; N. Sénégond; M. A. P. Pertijs;
In Proc. European Solid-State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC),
pp. 325--328, October 2019.
Abstract: ...
This paper presents a compact programmable high-voltage (HV) pulser for ultrasound imaging, designed for driving capacitive micro-machined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTs) in miniature ultrasound probes. To enable bipolar return-to-zero pulsing and embedded transmit/receive switching, a compact back-to-back isolating HV switch is proposed that employs HV floating-gate drivers with only one HV MOS transistor each. The pulser can be digitally programmed to generate bipolar pulses with and without return-to-zero, with a peak-to-peak swing up to 60 V, as well as negative and positive unipolar pulses. It can generate bursts of up to 63 pulses, with a maximum pulse frequency of 9 MHz for an 18 pF transducer capacitance. Realized in TSMC 0.18 μm HV BCD technology, the pulser occupies only 0.167 mm2. Electrical characterization results of the pulser, as well as acoustic results obtained in combination with a 7.5-MHz CMUT transducer, are presented. - A quantitative study on the impact of bit errors on image quality in ultrasound probes with in-probe digitization
Z. Chen; M. Soozande; H. J. Vos; J. G. Bosch; M. Verweij; N. de Jong; M. Pertijs;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
IEEE, October 2018. (abstract).
Abstract: ...
Integrating ultrasound transducers with ASICs which digitize and multiplex the received echo signals effectively mitigates the burden of signal transmission for 3-D catheter-based or endoscopic probes. Multiplexing the echo signals from multiple elements onto a cable reduces the cable count, but requires a higher data rate per cable, which typically involves a trade-off between power consumption and bit-error rate (BER). Understanding the impact of finite BER on the resulting image quality is a necessity to optimize the cable count and power consumption. In this work, this impact is quantitatively assessed using Matlab simulations. The effectiveness of error correction is also investigated. - Virtually Extended Array imaging improves lateral resolution in high frame rate volumetric imaging
M. Soozande; F. Fool; M. Shabanimotlagh; M. Pertijs; M. Verweij; H. J. Vos; J. G. Bosch; N. de Jong;
In Proc. IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS),
IEEE, pp. 1-4, October 2018. DOI: 10.1109/ULTSYM.2018.8580018
Abstract: ...
Matrix arrays for endoscopic and catheter-based applications are restricted to small physical apertures, which limits their lateral resolution. In addition, when aiming for high volume rate imaging and utilizing the recent methods of transmitting a single or few diverging waves (DW), lateral resolution further deteriorates. In this work, we propose a high frame rate transmission scheme which outperforms alternative methods in lateral resolution. To improve the lateral resolution and side-lobe level, we propose to transmit only on a sub-aperture on either side of the array and apply a specific weighting function to received data. Compared to single-DW imaging, the proposed Sub-aperture Virtually Extended Array reduces the PSF width and sidelobe level by 16% and 5dB respectively and provides a similar SNR at the cost of halving the frame rate.
BibTeX support